A web crawler, often referred to as a web spider, is an automated program designed to navigate the internet systematically. It begins its journey with a list of initial URLs, known as seed URLs, and proceeds to access these web pages. Once a page is visited, the crawler parses its HTML code to extract relevant information, such as text, links, and metadata. These extracted links lead to other web pages, which are then added to a queue for future exploration. The process continues recursively, allowing the crawler to cover vast areas of the web, making it a crucial tool for tasks like search engine indexing and data collection.
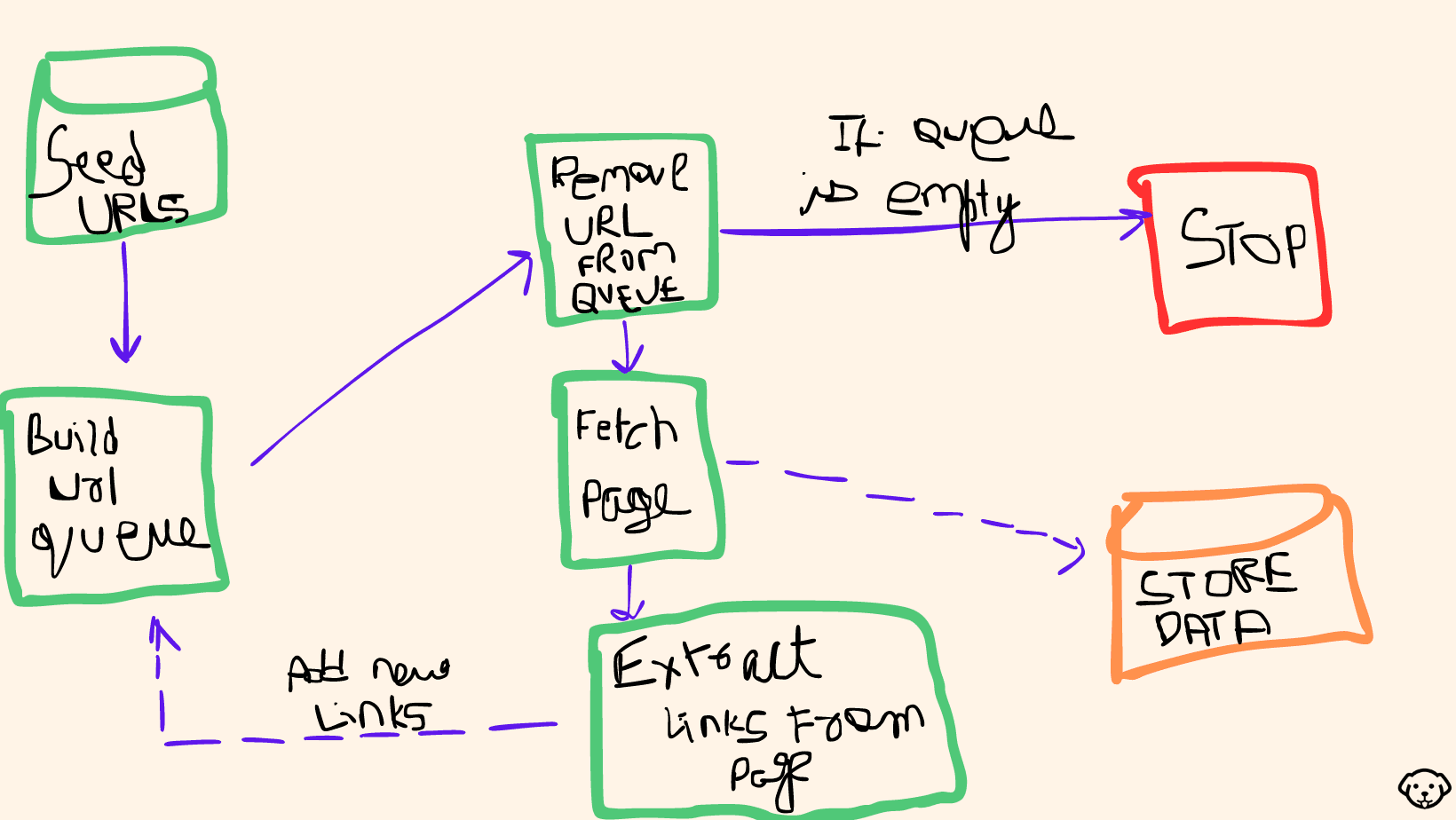
Web crawlers operate efficiently by adhering to guidelines set by websites in their robots.txt files and by maintaining crawl rate limits to avoid overloading web servers. They play a pivotal role in organizing and indexing the vast amount of information available on the internet, making it accessible to users through search engines and supporting various data-related tasks.
We have also written a complete guide on web crawling with Python. This guide can help you begin your journey with web crawling.