Google Scraping is one of the best methods to get comprehensive data from SERPs, as it provides insights into trends, competition, and consumer behavior.
Being one of the largest search engines, Google contains enormous data valuable for businesses and researchers.
However, to efficiently and effectively scrape Google search results, your data pipeline must be robust, scalable, and capable of handling dynamic changes in Google’s structure.
Whether you are looking to build your own LLM model or you are trying to gain some insight from the market, a Google search scraper would be needed.
In this read, we will build a Google search result scraper from scratch using Python and the BeautifulSoup library, enabling you to automate data extraction and gain actionable insights from search engine data.
But let’s see some common use cases one can have to use a Google scraper.
Use Cases of Scraping Google Search Results
- Analyze the latest market trends.
- Build your own LLM model.
- Scrape Google Ads data.
- Price competitive intelligence.
- Build a Rank Tracking System/Tool.
- Extract Emails by Scraping Google Search Results.
Why Python for Scraping Google Search Results?
Python is a widely used & simple language with built-in mathematical functions & hence is considered one of the best languages for scraping. Web scraping with Python is one of the most demanding skills in 2025 because AI is on a boom. It is also flexible and easy to understand even if you are a beginner. Plus the community is very big which helps if you face any syntax error during your initial days of coding.
Many forums like StackOverflow, GitHub, etc already have the answers to the errors you might face while coding when you scrape Google search results.
You can do countless things with Python but for now, we will learn web scraping Google search results with it.
Requirements
I hope Python is already installed on your computer, if not then you can download it from here. Create a folder to keep Python scripts in it.
mkdir google
We will need to install two libraries.
selenium– It is a browser automation tool. It will be used with Chromedriver to automate the Google Chrome browser. You can download the Chrome driver from here.BeautifulSoup– This is a parsing library. It will be used to parse important data from the raw HTML data.pandas– This library will help us store the data inside a CSV file.
pip install beautifulsoup4 selenium pandas
Now, create a Python file. We will write our script in this file. I am naming the file as search.py.
Why Selenium
Scraping Google with Python and Selenium
In this article, we are going to scrape this page. Of course, you can pick any Google query. Before writing the code let’s first see what the page looks like and what data we will parse from it.
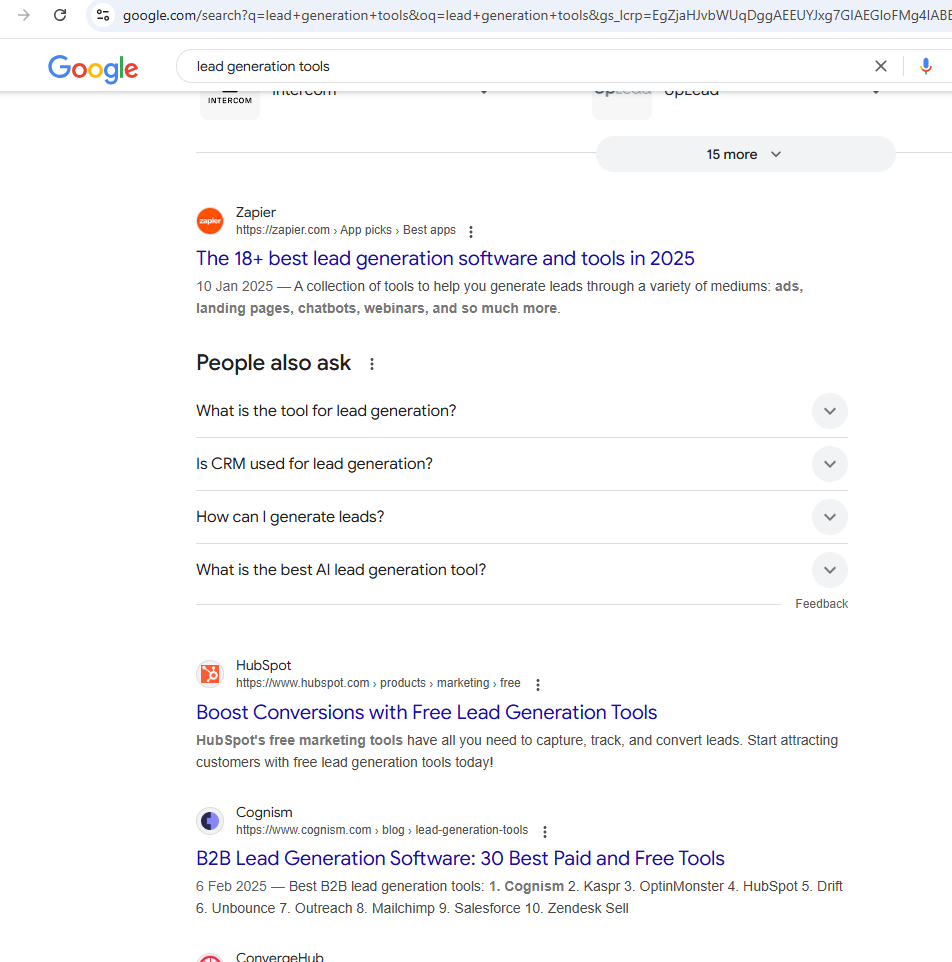
The page will look different in different countries.
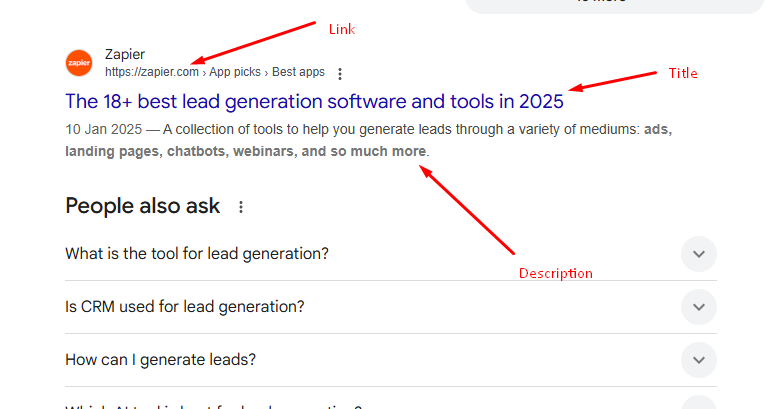
We are going to extract the link, title, and description from the target Google page. Let’s first create a basic Python script that will open the target Google URL and extract the raw HTML from it.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import time
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Set path to ChromeDriver (Replace this with the correct path)
CHROMEDRIVER_PATH = "D:/chromedriver.exe" # Change this to match your file location
# Initialize WebDriver with Service
service = Service(CHROMEDRIVER_PATH)
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument("--window-size=1920,1080") # Set window size
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
# Open Google Search URL
search_url = "https://www.google.com/search?q=lead+generation+tools&oq=lead+generation+tools"
driver.get(search_url)
# Wait for the page to load
time.sleep(2)
page_html = driver.page_source
print(page_html)
Let me briefly explain the code
- First, we have imported all the required libraries. Here
selenium.webdriveris controlling the web browser andtimeis for sleep function. - Then we have defined the location of our chromedriver.
- Created an instance of
chromedriverand declared a few options. - Then using
.get()function we open the target link. - Using
.sleep()function we are waiting for the page to load completely. - Then finally we extract the HTML data from the page.
Let’s run this code.

Yes yes, I know you got a captcha. Here I want you to understand the importance of using options arguments. While scraping Google you have to use — disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled. This Chrome option hides the fact that a browser is being controlled by Selenium, making it less detectable by anti-bot mechanisms. This also hides fingerprints.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import time
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Set path to ChromeDriver (Replace this with the correct path)
CHROMEDRIVER_PATH = "D:/chromedriver.exe" # Change this to match your file location
# Initialize WebDriver with Service
service = Service(CHROMEDRIVER_PATH)
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument("--window-size=1920,1080") # Set window size
options.add_argument("--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
# Open Google Search URL
search_url = "https://www.google.com/search?q=lead+generation+tools&oq=lead+generation+tools"
driver.get(search_url)
# Wait for the page to load
time.sleep(2)
page_html = driver.page_source
print(page_html)
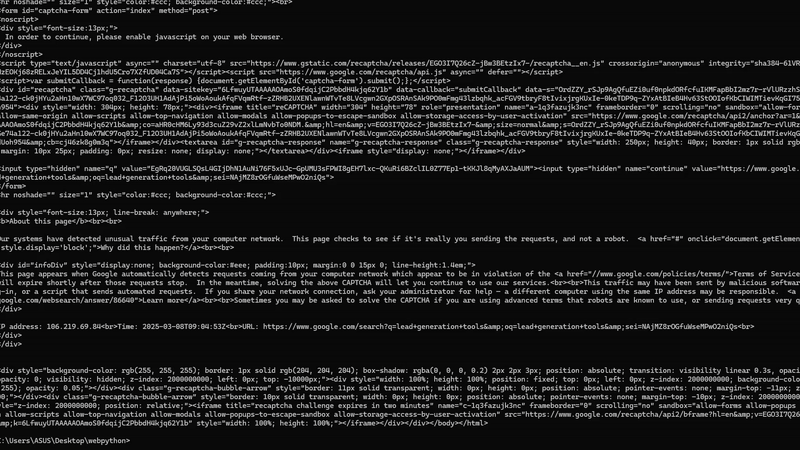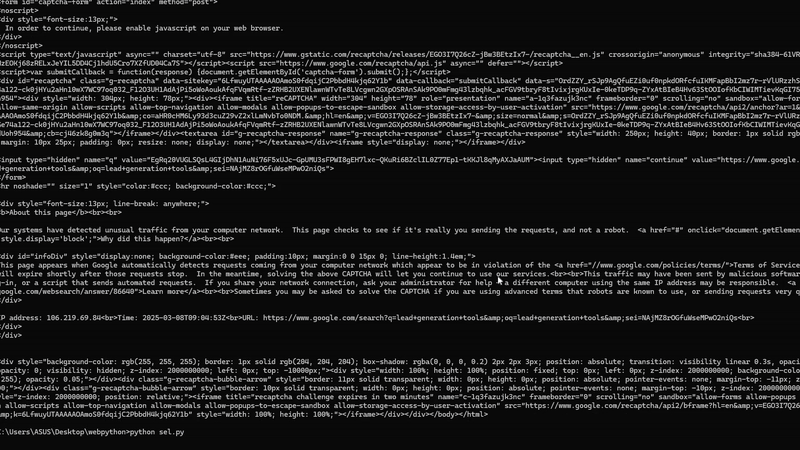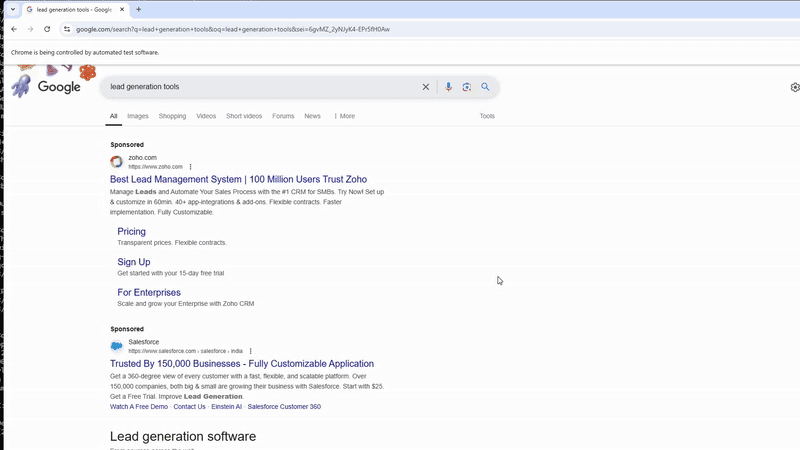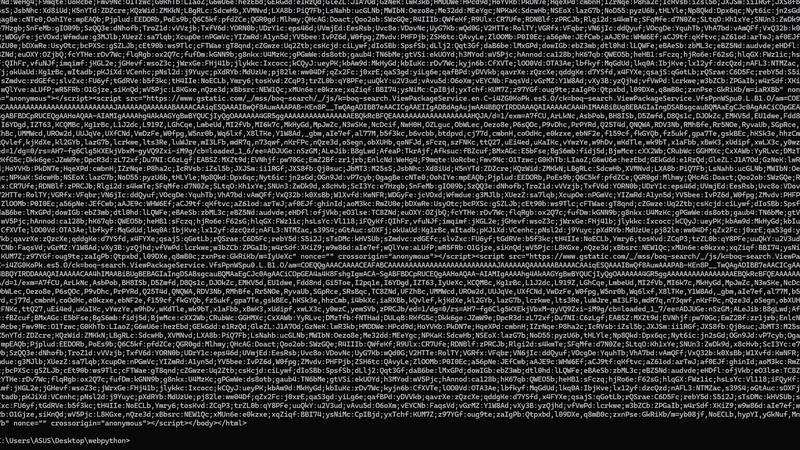
As expected we were able to scrape Google with that argument. Now, let’s parse it.
Parsing HTML with BeautifulSoup
Before parsing the data we have to find the DOM location of each element.
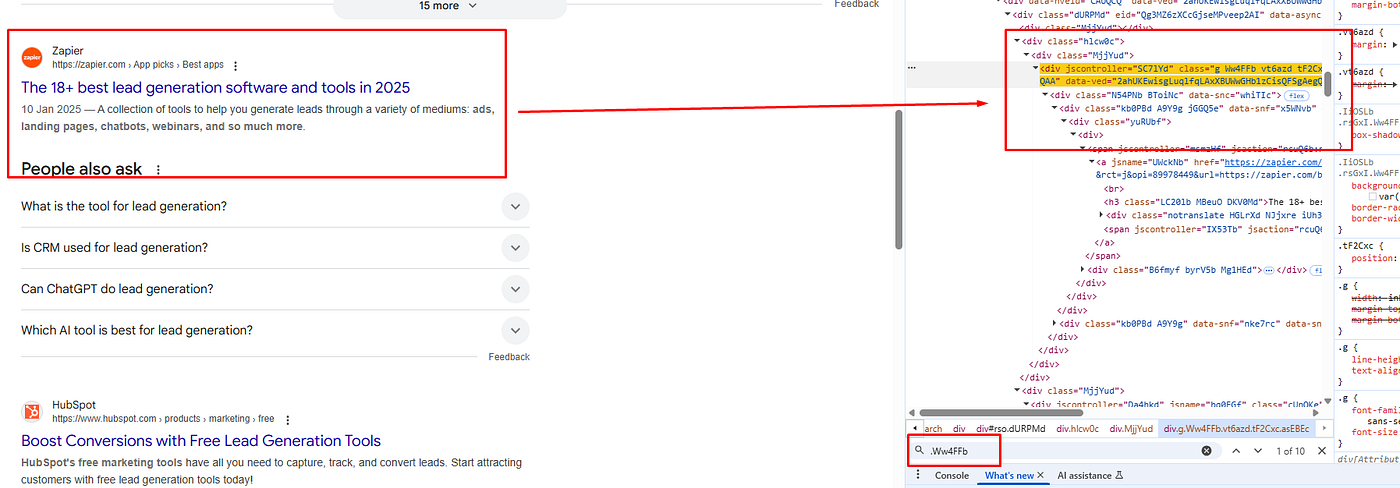
All the organic results have a common class Ww4FFb. All these organic results are inside the div tag with the class dURPMd.

The link is located inside the a tag.

The title is located inside the h3 tag.
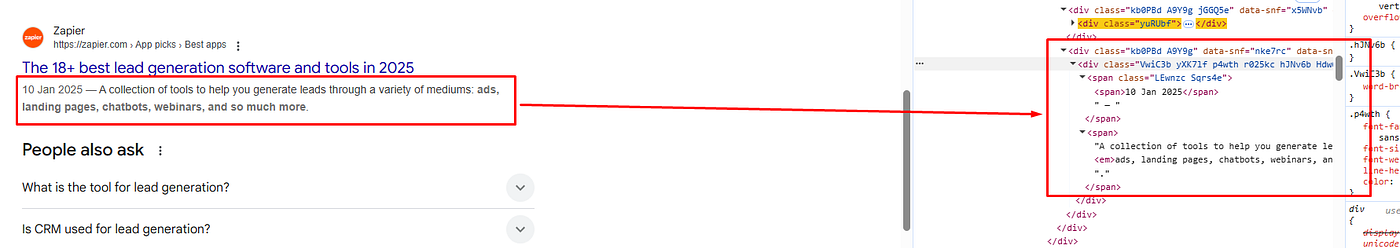
The description is located inside the div tag with the class VwiC3b. Let’s code it now.
page_html = driver.page_source
obj={}
l=[]
soup = BeautifulSoup(page_html,'html.parser')
allData = soup.find("div",{"class":"dURPMd"}).find_all("div",{"class":"Ww4FFb"})
print(len(allData))
for i in range(0,len(allData)):
try:
obj["title"]=allData[i].find("h3").text
except:
obj["title"]=None
try:
obj["link"]=allData[i].find("a").get('href')
except:
obj["link"]=None
try:
obj["description"]=allData[i].find("div",{"class":"VwiC3b"}).text
except:
obj["description"]=None
l.append(obj)
obj={}
print(l)
In the allData variable, we have stored all the organic results present on the page. Then using the for loop we are iterating over all the results. Lastly, we are storing the data inside the object obj and printing it.
Once you run the code you will get a beautiful JSON response like this.
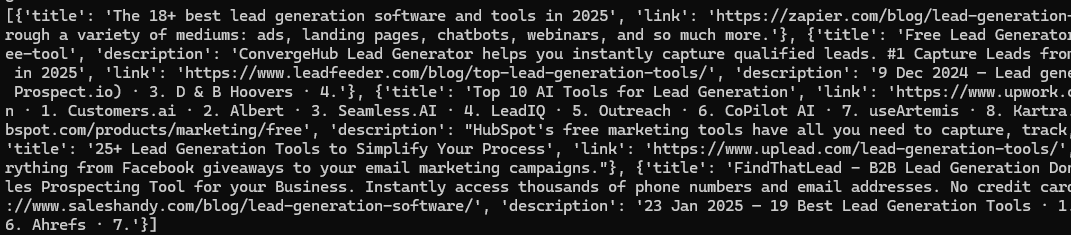
Finally, we were able to scrape Google and parse the data.
Storing data to a CSV file
We are going to use the pandas library to save the search results to a CSV file.
The first step would be to import this library at the top of the script.
import pandas as pd
Now we will create a pandas data frame using list l
df = pd.DataFrame(l)
df.to_csv('google.csv', index=False, encoding='utf-8')
Again once you run the code you will find a CSV file inside your working directory.
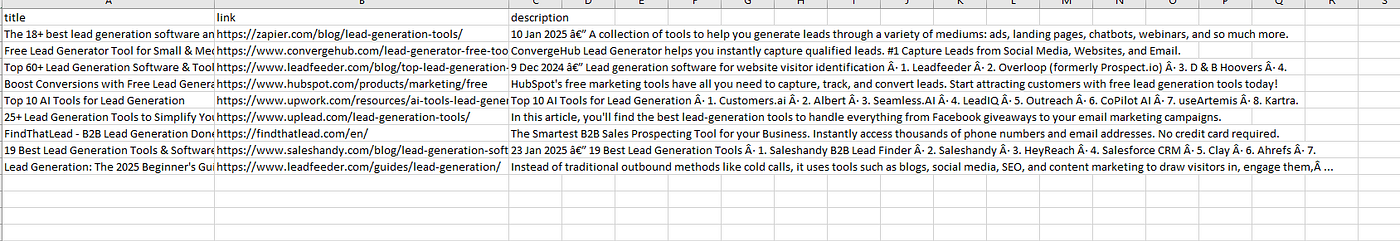
Complete Code
You can surely scrape many more things from this target page, but currently, the code will look like this.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import time
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
# Set path to ChromeDriver (Replace this with the correct path)
CHROMEDRIVER_PATH = "D:/chromedriver.exe" # Change this to match your file location
# Initialize WebDriver with Service
service = Service(CHROMEDRIVER_PATH)
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument("--window-size=1920,1080") # Set window size
options.add_argument("--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options)
# Open Google Search URL
search_url = "https://www.google.com/search?q=lead+generation+tools&oq=lead+generation+tools"
driver.get(search_url)
# Wait for the page to load
time.sleep(2)
page_html = driver.page_source
soup = BeautifulSoup(page_html,'html.parser')
obj={}
l=[]
allData = soup.find("div",{"class":"dURPMd"}).find_all("div",{"class":"Ww4FFb"})
print(len(allData))
for i in range(0,len(allData)):
try:
obj["title"]=allData[i].find("h3").text
except:
obj["title"]=None
try:
obj["link"]=allData[i].find("a").get('href')
except:
obj["link"]=None
try:
obj["description"]=allData[i].find("div",{"class":"VwiC3b"}).text
except:
obj["description"]=None
l.append(obj)
obj={}
df = pd.DataFrame(l)
df.to_csv('google.csv', index=False, encoding='utf-8')
print(l)
Well, this approach is not scalable because Google will block all the requests after a certain number of requests. We need some advanced scraping tools to overcome this problem.
Limitations of scraping Google search results with Python
Although the above approach is great if you are not looking to scrape millions of pages. But if you want to scrape Google at scale then the above approach will fall flat and your data pipeline will stop working immediately. Here are a few reasons why your scraper will be blocked.
- Since we are using the same IP for every request, Google will ban your IP, which will result in the blockage of the data pipeline.
- Along with IPs, we need quality headers and multiple browser instances which are absent in our approach.
The solution to the above problem will be using a Google Search API like Scrapingdog. With Scrapingdog you don’t have to worry about proxy rotations or retries. Scrapingdog will handle all the hassle of proxy and header rotation and seamlessly deliver the data to you.
You can scrape millions of pages without getting blocked with Scrapingdog. Let’s see how we can use Scrapingdog to scrape Google at scale.
Scraping Google Search Results with Scrapingdog
Now, that we know how to scrape Google search results using Python and Beautifulsoup, we will look at a solution that can help us scrape millions of Google pages without getting blocked.
We will use Scrapingdog’s Google Search Result Scraper API for this task. This API handles everything from proxy rotation to headers. You just have to send a GET request and in return, you will get beautiful parsed JSON data.
This API offers a free trial and you can register for that trial from here. After registering for a free account you should read the docs to get the complete idea of this API.
import requests
api_key = "Paste-your-own-API-key"
url = "https://api.scrapingdog.com/google/"
params = {
"api_key": api_key,
"query": "lead generation tools",
"results": 10,
"country": "us",
"page": 0
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
print(data)
else:
print(f"Request failed with status code: {response.status_code}")
The code is pretty simple. We are sending a GET request to https://api.scrapingdog.com/google/ along with some parameters. For more information on these parameters, you can again refer to the documentation.
Once you run this code you will get a beautiful JSON response.
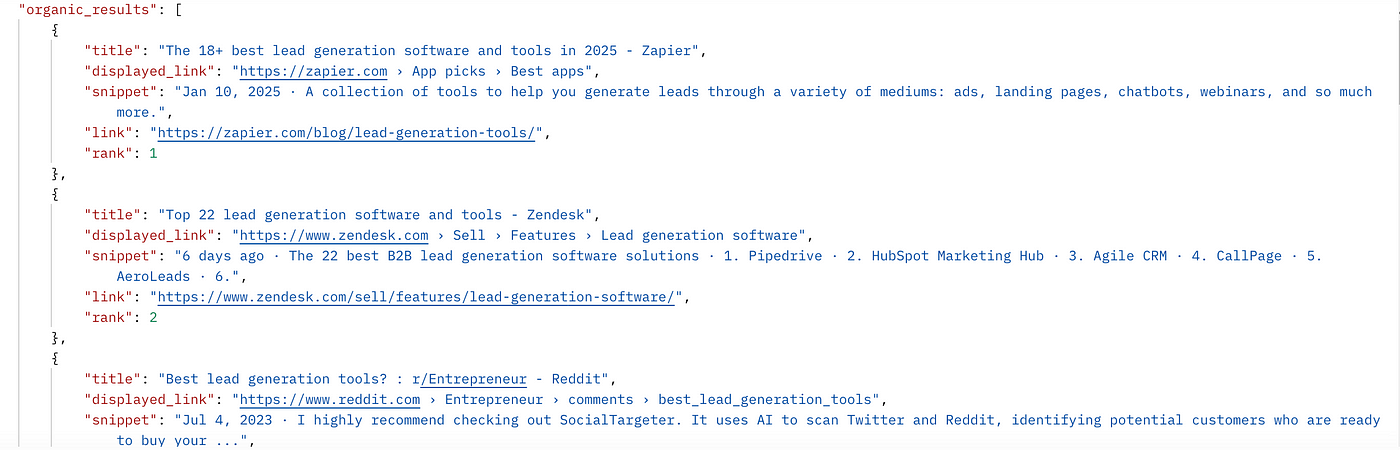
In this JSON response, you will get People also ask for data & related search data as well. So, you are getting full data from Google not just organic results.
What if I need results from a different country?
As you might know, Google shows different results in different countries for the same query. Well, I just have to change the country parameter in the above code.
Let’s say you need results from the United Kingdom. For this, I just have to change the value of the country parameter to gb(ISO code of UK).
You can even extract 100 search results instead of 10 by just changing the value of the results parameter.
Here’s a video tutorial on how to use Scrapingdog’s Google SERP API.⬇️
How To Scrape Google ADs using Scrapingdog's Search API
Yes, you can use Scrapingdog’s SERP API to extract competitors’ AD results.
In the documentation, you can read about the 'advance_search' parameter. This parameters allows you to get advanced SERPs results and Google Ads results are there in it.
I have made a quick tutorial too, to make you understand how Google SERP API can be used to get ADs data.⬇️
Is there an official Google SERP API?
Google offers its API to extract data from its search engine. It is available at this link for anyone who wants to use it. However, the usage of this API is minimal due to the following reasons: –
The API is very costly — For every 1000 requests you make, it will cost you around $5, which doesn’t make sense as you can do it for free with web scraping tools.
The API has limited functionality — It is made to scrape only a small group of websites, although by doing changes to it you can scrape the whole web again which would cost you time.
Limited Information — The API is made to provide you with little information, thus any data extracted may not be useful.
Conclusion
In this article, we saw how we can scrape Google results with Python and BS4. Then we used web scraping API for scraping Google at scale without getting blocked.
Google has a sophisticated anti-scraping wall that can prevent mass scraping but Scrapingdog can help you by providing a seamless data pipeline that never gets blocked.
If you like this article please do share it on your social media accounts. If you have any questions, please contact me at [email protected].
Frequently Asked Questions
When you send Google request from the same IP, it ultimately bans you. However, by using a Google scraper API, you can scrape the Google search results fast and without getting blocked.
The legality of scraping Google search data is largely discussed in the scraping field. Scraping publicly available data on the internet – including Google SERP data – is legal.
You can read more about the legality of web scraping in general here.
Additional Resources
- Scrape Bing Search Results using Python (A Detailed Tutorial)
- Web Scraping Google News using Python
- How To Web Scrape Google Autocomplete Suggestions
- 10 Best Google SERP Scraper APIs
- 6 Best Rank Tracking APIs
- Web Scraping Google Maps using Python
- Web Scraping Google Images using Python
- Web Scraping Google Scholar using Python
- Web Scraping Google Shopping using Python
- How To Scrape People Also Ask using Google Search API
- How to Scrape Google Local Results using Python & Scrapingdog API
Web Scraping with Scrapingdog


